2,4-Dichloro-5-Sulfamoylbenzoic Acid CAS 2736-23-4 Furosemide Intermediate Factory
Furosemide and Related Intermediates:
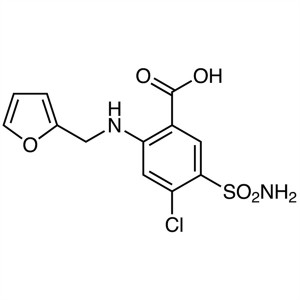
Furosemide CAS 54-31-9
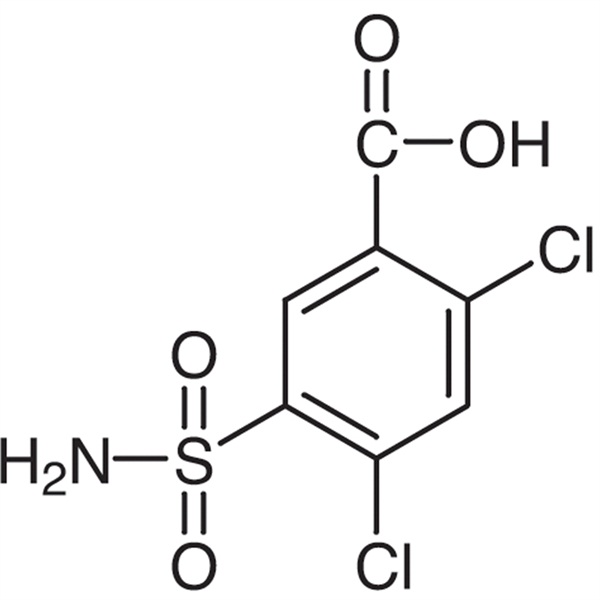
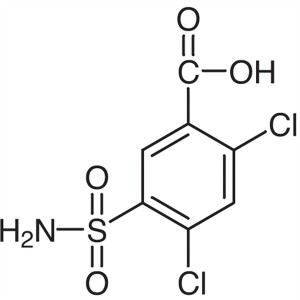
2,4-Dichloro-5-Sulfamoylbenzoic Acid CAS 2736-23-4
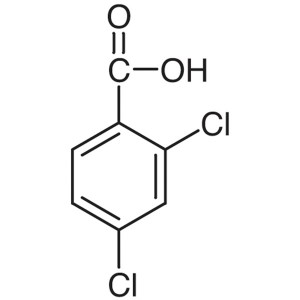
2,4-Dichlorobenzoic Acid CAS 50-84-0
| Chemical Name | 2,4-Dichloro-5-Sulfamoylbenzoic Acid |
| Synonyms | 5-(Aminosulfonyl)-2,4-Dichlorobenzoic Acid |
| CAS Number | 2736-23-4 |
| CAT Number | RF-PI431 |
| Stock Status | In Stock, Production Scale Up to Tons |
| Molecular Formula | C7H5Cl2NO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 270.08 |
| Brand | Ruifu Chemical |
| Item | Specifications |
| Appearance | White or Off-White Crystalline |
| Assay | ≥99.0% |
| Melting Point | 230.0~235.0℃ |
| Moisture (K.F) | ≤0.50% |
| Residue on Ignition | ≤0.20% |
| 2,4-Dichlorobenzoic Acid | ≤0.50% |
| Total Impurities | ≤1.0% |
| Test Standard | Enterprise Standard |
| Usage | Intermediate of Furosemide (CAS 54-31-9), Diuretic |
Package: Bottle, Aluminium foil bag, 25kg/Cardboard Drum, or according to customer's requirement.
Storage Condition: Store in sealed containers at cool and dry place; Protect from light and moisture.


2,4-Dichloro-5-Sulfamoylbenzoic Acid (CAS 2736-23-4) is a chlorinated sulfamoylbenzoic acid with diuretic acid. 2,4-Dichlorobenzoic Acid (CAS 50-84-0) by sulfochlorination, ammoniation, acidification, 2,4-Dichloro-5-Sulfamoylbenzoic Acid is obtained. Then after condensation with the chaff amine, Furosemide (CAS 54-31-9) is produced. Furosemide inhibits ion co-transport in the kidney. Furosemide is used as a diuretic. Furosemide, is a class of efficient sulfonamide diuretics acting on the medullary loop of the ascending branch of the medulla,it has a strong and short-term diuretic effect,which can increase the excretion of water, sodium, chloride, potassium, calcium, magnesium, phosphate and so on. It Mainly inhibits Na + and Cl-reabsorption in medullary and cortex of the medullary loop ascending branch crude segment , it can promote the excretion of sodium, chloride and potassium and affect the formation of renal medullary high osmotic pressure,it can interfer the process of concentration and dilution of urine, and it can increase urine output.